Balloon Framed Wall – Framed walls (generally over 10′ tall) that run the entire vertical length from the floor sill plate to the roof. This is done to eliminate the need for a gable end truss.
Baluster – Vertical member in a railing used between a top rail and bottom rail or the stair treads. Sometimes referred to as a ‘picket’ or ‘spindle’.
Column- A vertical structural compression member which supports loads.
Crawl Space – A shallow space below the living quarters of a house, normally enclosed by the foundation wall and having a dirt floor.
Damp-proofing – Black, tar like waterproofing material applied to the exterior of a foundation wall.
Dormer – An opening in a sloping roof, the framing of which projects out to form a vertical wall suitable for windows or other openings.
Downspout – A pipe, usually of metal, for carrying rainwater down from the roof’s horizontal gutters.
Drywall – A manufactured panel made out of gypsum plaster and encased in a thin cardboard. Usually 1/2″ thick and 4′ x 8′ or 4′ x 12′ in size. The panels are nailed or screwed onto the framing and the joints are taped and covered with a ‘joint compound’. ‘Green board’ type drywall has a greater resistance to moisture than regular (white) plasterboard and is used in bathrooms and other “wet areas”.
Duct – A round or rectangular metal pipe installed for distributing warm (or cold) air from the furnace to rooms in the home. Also, a tunnel made of galvanized metal or rigid fiberglass that carries air from the heater or ventilation opening to the rooms in a building.
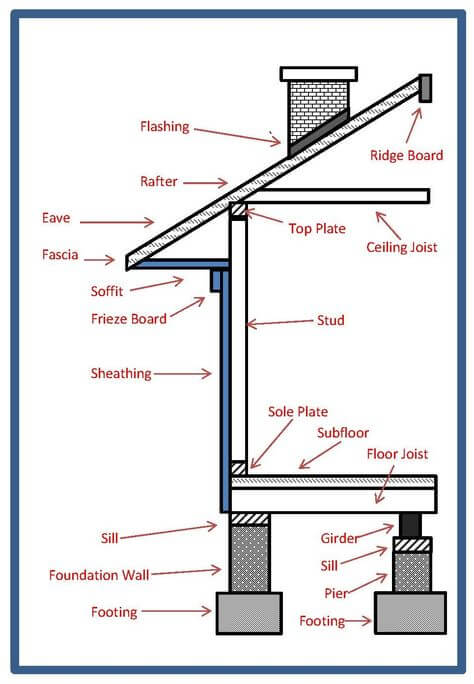
Eaves – The horizontal exterior roof overhang.
Fascia – Horizontal boards attached to rafter/truss ends at the eaves and along gables. Roof drain gutters are attached to the fascia.
Footing – Continuous 8″ or 10″ thick concrete pad installed before and supports the foundation wall.
Form – Temporary structure erected to contain concrete during placing and initial hardening.
Foundation – The supporting portion of a structure below the first floor construction, or below grade, including the footings.
Framing – Lumber used for the structural members of a building, such as studs, joists and rafters.
Gable – The upper triangular-shaped portion of an end wall, beneath the roof.
Gable Roof – A ridge roof which terminates in a gable.
Gingerbread – Wood trim or molding of an elaborate ornamentation or superfluous embellishment.
Insulation – Any material high in resistance to heat transmission that, when placed in the walls, ceiling or floors of a structure, will reduce the rate of heat flow.
Jamb – The side and head lining of a doorway, window or other opening. Includes studs as well as the frame and trim.
Joist – Wooden 2 X 8’s, 10’s or 12’s that run parallel to one another and support a floor or ceiling, and supported in turn by larger beams, girders or bearing walls.
Millwork – Generally all building materials made of finished wood and manufactured in millwork plants. Includes all doors, window and door frames, blinds, mantels, panelwork, stairway components (ballusters, rails, etc.), moldings and interior trim. Does not include flooring, ceiling or siding.
Post and Pad Foundation – A foundation assembly for supporting a cross member that comprises a vertical timber post attached to the upper surface of a wider pre-formed concrete pad.
Rafter – Lumber used to support the roof sheeting and roof loads. Generally, 2 X 10’s and 2 X 12’s are used. The rafters of a flat roof are sometimes called roof joists.
Soffit – The area below the eaves and overhangs. The underside where the roof overhangs the walls. Usually the underside of an overhanging cornice.
Slab – Concrete pavement, including driveway, garage, and basement floor.
Stud – A vertical wood framing member, also referred to as a wall stud, attached to the horizontal sole plate below and the top plate above. Normally 2 X 4’s or 2 X 6’s, 8′ long. One of a series of wood or metal vertical structural members placed as supporting elements in walls and partitions.
Sump Pump – A submersible pump in a sump pit that pumps any excess ground water to the outside of the home.
Turret – A small tower projecting from a building, usually at a corner.
Vancouver Special – A common reference to houses built in a particular architectural styleroughly between 1965 and 1985 in Vancouver, B.C. They are characterized by their box-like structure, low-pitched roofs, balconies across the front of the house, and brick or stone finishes on the ground-floor level of the facade with stucco elsewhere. Vancouver Specials usually have the main living quarters on the upper floor and secondary bedrooms on the bottom, making them ideal for renovating to secondary suites. The style takes maximum advantage of the buildable area of a standard city lot.
Vapour Barrier – A building product installed on exterior walls and ceilings under the drywall and on the warm side of the insulation. It is used to retard the movement of water vapour into walls and prevent condensation within them. Normally, polyethylene plastic sheeting is used.